Faculty Profile: Niel Brandt
|
Niel Brandt Distinguished Professor of Astronomy & Astrophysics 514A Davey Lab Phone: +1 814-865-3509 Email: niel@astro.psu.edu |
 |
Research Interests:
W. Niel Brandt has been at Penn State since 1997 and is currently a Distinguished Professor in the Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics. His main areas of research include (1) active galaxies and quasars, (2) cosmological X-ray and multiwavelength surveys, and (3) high-energy astrophysics. Since 1999 he has been using the Chandra X-ray Observatory and the X-ray Multi-Mirror Mission-Newton to study the physics, evolution, and ecology of active galaxies and other cosmic X-ray sources. He also utilizes data from a variety of other projects, including the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), and in the future he plans to study active galaxies with the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST). Some of the key research questions he is working to address are the following:
- What physical processes control the spectra and variability of active galaxies, both at high energies and across the electromagnetic spectrum?
- How powerful are the winds from active galactic nuclei? How have these winds shaped typical massive galaxies?
- What is the demography of the accreting supermassive black hole population over cosmic time, especially in the most highly obscured systems?
- How did the first supermassive black holes in the Universe feed and grow?
- How have the X-ray properties of starburst and normal galaxies evolved over cosmic time, and what does this imply about the evolution of their accreting X-ray binary populations?
Research Milestones and Discoveries
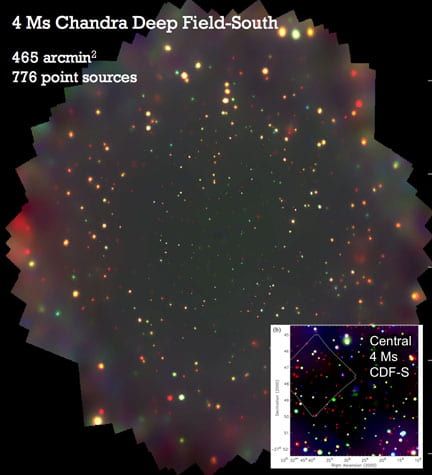
Creation of the most sensitive X-ray surveys of the extragalactic universe. These have significantly constrained the cosmic growth of supermassive black holes, determined the importance of black-hole accretion within the overall cosmic energy budget, measured the active galactic nucleus content of forming massive galaxies, and detected X-ray emission from cosmologically distant starburst and normal galaxies.
Studies of winds from active galaxies, ranging from local Seyfert galaxies to distant quasars. X-ray gratings studies of Seyfert winds have utilized hundreds of detected atomic features to provide qualitatively new information about wind physical conditions, kinematics, and geometry, and X-ray spectroscopy of distant quasars has clarified their wind geometries, mass-ejection rates, and role in feedback.
X-ray observations of the first supermassive black holes in the Universe. My group has increased the number of X-ray detected active galaxies at z > 4 by more than an order of magnitude, showing that X-ray emission is a universal and stable property of accreting supermassive black holes out to the reionization epoch.
Research Facilities
Currently Utilized:
- Chandra X-ray Observatory
- XMM-Newton Mission
- Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Explorer
- Sloan Digital Sky Survey-III
- Hobby-Eberly Telescope
- Spitzer Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
Upcoming:
- Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR)
- Large Synoptic Survey Telescope
